CRB Monitor Chart of the Month: The SEC Approves Eleven New Spot Bitcoin ETFs
James B. Francis, CFA, Chief Research Officer, CRB Monitor
Peter Simcox, Senior Analyst, CRB Monitor
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has recently approved eleven spot Bitcoin-based exchange traded funds marking a historic milestone for the crypto industry, the ETF market, and investors. Now actively trading for the last few weeks, these vehicles allow US investors to gain daily exposure to the world’s largest and most liquid cryptocurrency without directly holding it, and as a result they simplify and reduce some of the risk related to the process of investing in Bitcoin (BTC). SEC approval of these ETFs has been on the radar of CRB Monitor research for several months, and this latest development, the listing of the following 11 exchange traded funds, has resurrected interest in digital assets by the institutional and retail investment communities.
The following table has some of the key pieces of information regarding these new ETFs:
|
US-Listed Bitcoin ETFs - As of 1/31/2024 |
||||||
|
Primary Exchange |
Ticker |
ETF Name |
Fund Type |
AUM (USD MM) |
Expense Ratio** |
Digital Asset Custodian |
|
NYSE Arca |
Spot |
$20,708.07 |
1.50% |
Coinbase Custody Trust Company, LLC |
||
|
NYSE Arca |
Spot* |
$17.18 |
0.92% |
BitGo Trust Company, Inc |
||
|
Cboe BZX |
Spot |
$60.89 |
0.19% |
Coinbase Custody Trust Company, LLC |
||
|
Cboe BZX |
Spot |
$126.09 |
0.25% |
Gemini Trust Company, LLC |
||
|
NASDAQ |
Spot |
$2,720.49 |
0.25% |
Coinbase Custody Trust Company, LLC |
||
|
NASDAQ |
Spot |
$112.92 |
0.25% |
Coinbase Custody Trust Company, LLC |
||
|
Cboe BZX |
Spot |
$300.00 |
0.25% |
Coinbase Custody Trust Company, LLC |
||
|
Cboe BZX |
Spot |
$11.15 |
0.30% |
Coinbase Custody Trust Company, LLC |
||
|
Cboe BZX |
Spot |
$1,340.00 |
0.25% |
Fidelity Digital Asset Services, LLC |
||
|
Cboe BZX |
Spot |
$10.32 |
0.21% |
Coinbase Custody Trust Company, LLC |
||
|
NYSE Arca |
Spot |
$640.84 |
0.20% |
Coinbase Custody Trust Company, LLC |
||
|
* The Hashdex Bitcoin Futures ETF is in the process of being converted to a Bitcoin Spot ETF and renamed "Hashdex Bitcoin ETF" ** Expense Ratio after waiver period has ended |
||||||
[CRB Monitor provides extensive coverage of all securities that have any connection to the digital asset ecosystem, including the more than 300 exchange traded products (ETPs) that provide investors with digital asset exposure.]
Some Key Information About Spot Bitcoin ETFs
An ETF is, in essence, a mutual fund that is listed and traded on an exchange, giving investors and traders the benefit of real-time pricing and intraday execution. [There are several other aspects of ETF mechanics that further differentiate them from mutual funds, but we will not detail them here.]
Spot Bitcoin ETFs such as the 11 that have recently started trading invest directly in Bitcoin (BTC), which is a departure from competing funds that achieve their exposure through futures or return swaps. In other words, this group of ETFs buys and sells actual Bitcoins which reside in a digital vault that is managed by a registered custodian. Shares in Bitcoin ETFs are created and redeemed via cash-settled (as opposed to in-kind) creations and redemptions, which removes some of the operational complexities and risks for authorized participants and market makers – but not the volatility and certainly not the regulatory concerns.
Spot Bitcoin ETFs offer several advantages over investing in the physical Bitcoins, whether it requires trading directly on a crypto exchange or through a peer-to-peer platform. These advantages include:
- Convenience: Investors can trade spot Bitcoin ETFs through brokerage accounts without having to deal with the technical and operational aspects of owning and storing Bitcoins, setting up a digital wallet, transferring funds, or securing private keys.
- Security: Investors do not have to worry about the risk of losing their Bitcoins due to hacking, theft, or human error, as the ETFs rely on professional and regulated custodians to safeguard the digital assets. The custodians also provide insurance coverage and regular audits to ensure the safety and transparency of the ETFs.
- Pricing: Bitcoin ETFs trade and price throughout the day on regulated exchanges while the underlying coins transact 24/7 with no central pricing source, making valuations a challenge.
How do these ETFs differ from one another?
What is interesting about the these 11 ETFs (please see the table above) is the broad range across the space with regard to both size and expense ratio. The range of assets under management (AUM) stretches from the barely viable Ark 21Shares Bitcoin ETF (Cboe BZX: ARKB) at $10 million to the clear leader (for now), the Grayscale Bitcoin Trust ETF (NYSE Arca: GBTC) at $21 billion. To be fair, GBTC had a head start, as this fund has been trading for more than a decade as a Bitcoin futures-based ETF and transitioned to a 100% spot ETF. Not surprisingly GBTC’s bloated AUM is shrinking, as investors have already begun their exodus out of them and into lower expense-ratio ETFs. But investors should proceed with caution as they sell out of GBTC in search of lower fee ETFs, as the tax consequences of this switch could eat up a significant portion of the savings.
Aside from the differences in expense ratio and AUM these 11 funds are very similar (perhaps identical in their construction), which is evidenced in the performance and the correlations displayed below.
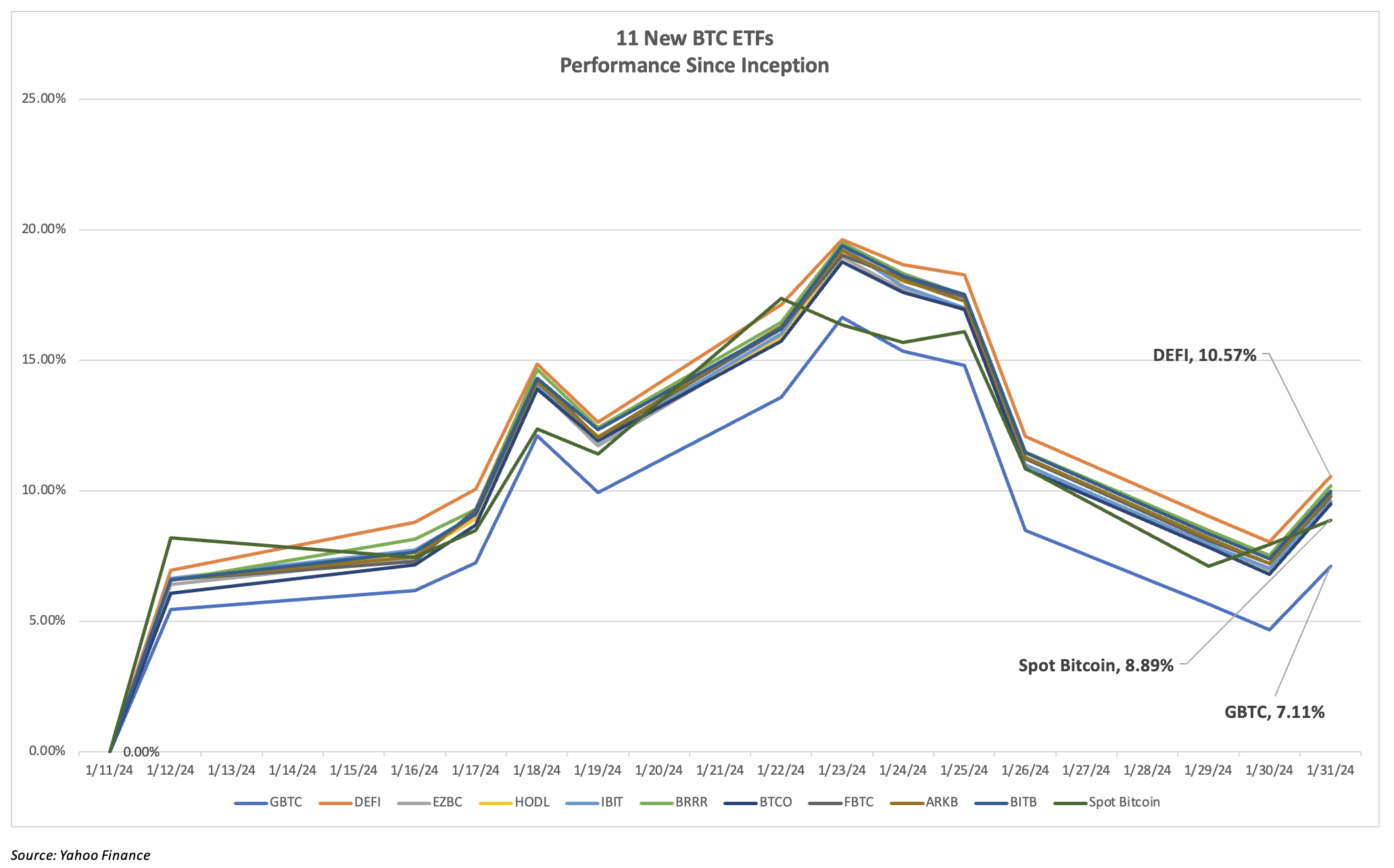
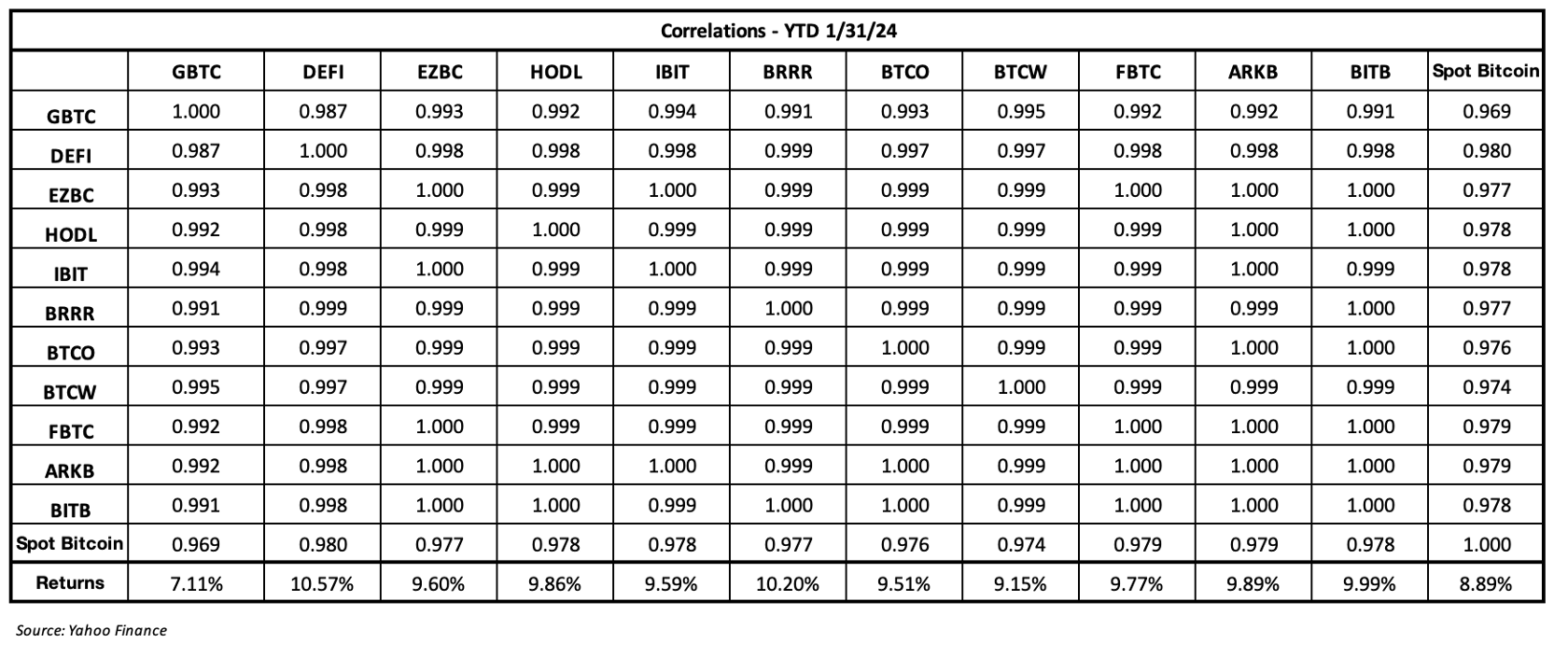
What are the chart and the table showing us? First, that investors should not worry about the relative performance of these ETFs and their tracking error vs. spot Bitcoin. Rather, we advise to select on the combination of high AUM and low expense ratio. On the performance chart above the only real outliers are GBTC, which has had an early sell-off of over $1 billion largely due to its outlier expense ratio (1.50%), and DEFI, which is still futures-based until it completes its transition to spot – [much of the positive tracking could be coming from the spreads of spot BTC vs. futures, but more investigation will be needed to confirm this.] However, aside from these two pricey outliers, the field looks very much like a dead heat in terms of its inception-to-date performance and correlation. And this is good news for investors, as apparently all they need to worry about related to selection are expense ratios and AUM. For all intents and purposes, these ETFs are essentially the same and should produce similar results.
Now for a few things to worry about, once you have decided to invest in spot Bitcoin ETFs.
Challenges Presented by Spot Bitcoin ETFs
Spot Bitcoin ETFs represent a significant opportunity for the crypto industry and for investors, as they provide a convenient, and cost-efficient way to access the world’s largest cryptocurrency. They also have the potential to attract new institutional and retail investors to the crypto space, increasing the liquidity, adoption, and credibility of Bitcoin.
However, spot Bitcoin ETFs also face a number of challenges and risks to investors, given that the ETFs will not provide cover from the embedded risks that are inherent in the digital asset industry. For example, the prospectus for the iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT) describes a critical aspect of the create/redeem process as follows:
"The Trust will create Shares by receiving Bitcoin from a third party that is not the Authorized Participant and the Trust—not the Authorized Participant—is responsible for selecting the third party to deliver the Bitcoin. Further, the third party will not be acting as an agent of the Authorized Participant with respect to the delivery of the Bitcoin to the Trust or acting at the direction of the Authorized Participant with respect to the delivery of the Bitcoin to the Trust. The Trust will redeem Shares by delivering Bitcoin to a third party that is not the Authorized Participant and the Trust—not the Authorized Participant—is responsible for selecting the third party to receive the Bitcoin. Further, the third party will not be acting as an agent of the Authorized Participant with respect to the receipt of the Bitcoin from the Trust or acting at the direction of the Authorized Participant with respect to the receipt of the Bitcoin from the Trust. The third party will be unaffiliated with the Trust and the Sponsor...The Prime Execution Agent facilitates the purchase and sale or settlement of the Trust’s Bitcoin transactions. Bitcoin Trading Counterparties settle trades with the Trust using their own accounts at the Prime Execution Agent when trading with the Trust."
What all this suggests (and why investors should take note) is, because of the fractured nature of how digital assets transact, that the success of a critical link in the operational chain cannot be guaranteed. And while we will not go into the mechanics of typical, standard ETFs, suffice it to say that trade and settlement are not left to “unaffiliated third parties”.
And as such, we conclude that investors in these 11 new ETFs are subject to the same risks as investors in the underlying digital assets themselves:
- Regulatory uncertainty: The SEC has approved the spot Bitcoin ETFs under the condition that they comply with the Securities Act of 1933, the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934, and the Commission’s rules regarding cryptocurrency. However, the SEC has also expressed its skepticism and caution about the crypto industry, and has warned investors about the risks involved in investing in Bitcoin and crypto-related products. The SEC may also impose additional requirements or restrictions on the spot Bitcoin ETFs in the future, or even revoke their approval, depending on the market conditions and the regulatory environment.
- Market volatility: Bitcoin is known for its high volatility, as its price can fluctuate significantly in a short period of time, due to various factors such as supply and demand, news and events, speculation, and manipulation. Investing in spot Bitcoin ETFs exposes investors to the same volatility risk as investing in Bitcoin directly, and may result in substantial losses or gains. Investors should be prepared for the possibility of extreme price movements and have a long-term perspective when investing in spot Bitcoin ETFs.
- Operational risk: Spot Bitcoin ETFs rely on third-party custodians to store and safeguard the Bitcoins backing the ETFs. While these custodians are professional and regulated entities that provide insurance coverage and regular audits, investors should understand the underlying risks involved related to trade, pricing and settlement of the coins held by each ETF.
Finally, from the GBTC Factsheet risk disclosures: “Digital assets represent a new and rapidly evolving industry. The value of GBTC depends on the acceptance of the digital assets, the capabilities and development of blockchain technologies and the fundamental investment characteristics of th digital asset. Digital asset networks are developed by a diverse set of contributors and the perception that certain high-profile contributors will no longer contribute to the network could have an adverse effect on the market price of the related digital asset.”
BIS Digital Asset Classification
New challenges persist beyond the wide range of quality among digital asset regulators. Despite notable strides, risks endure, particularly in the global circulation and trading of digital assets. The heightened exposure of Bitcoin ETFs to underlying risks emphasizes the need for a comprehensive understanding of evolving standards.
As major financial institutions prepare for new Basel Committee on Banking Supervision standards by January 1, 2025, the landscape becomes more intricate, categorizing Cryptoassets into 4 risk classes (Group 1a & 1b and Group 2a & 2b), with the 2’s presenting higher levels of operating risk.
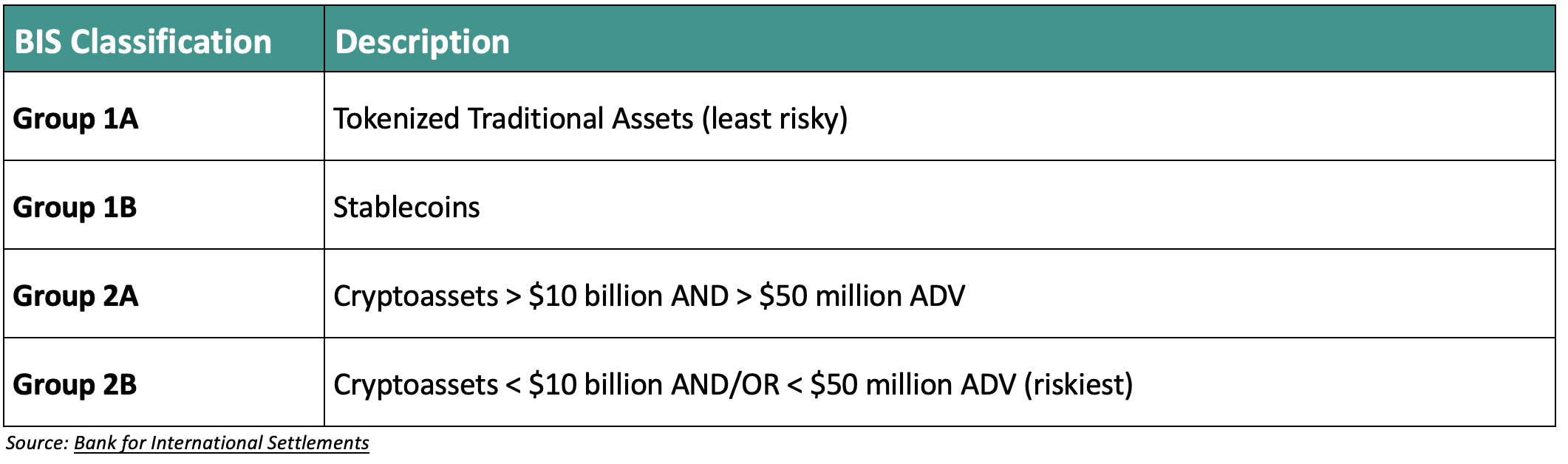
Bitcoin's placement in Group 2, specifically subgroup 2A, confirms the necessity for institutions to adapt risk management strategies that are in line with the elevated risk that is assigned by this new classification, which goes into effect in January 2025. This new set of standards would then place all spot Bitcoin ETFs in group 2A, given that Bitcoin is essentially all that they hold.
Why is this important? Because regulators will require financial institutions to report their exposure to Group 1 and Group 2 Cryptoassets as their exposure to them will be limited. In the words of the Basel report, “A bank’s total exposure to Group 2 Cryptoassets must not exceed 2% will apply the more conservative Group 2b capital treatment to the amount by which the limit is exceeded. Breaching the 2% limit will result in the whole of Group 2 exposures being subject to the Group 2b capital treatment of the bank’s Tier 1 capital and should generally be lower than 1%. Banks breaching the 1% limit.”
Global Regulatory Risk
While it is appropriate to describe the digital asset industry as “heavily” regulated, it is also accurate to describe digital asset regulation as “complicated”. Truth be told, there are now 100’s of regulatory agencies worldwide that are doing their best to keep up with several different categories of market participants, with varying degrees of success. But the reality is that, given its attraction for bad actors, regulating the crypto industry is a challenge and financial institutions that facilitate trading and custody of digital asset ETPs should be aware of this added layer of risk.
As such, CRB Monitor has developed a model which applies “quality” scores to many of the world’s largest licensing authorities. A summary of this model can be found in our August 2023 article Applying Risk Ratings to Digital Asset Regulators. In a nutshell, financial institutions are wedged between a rock and a hard place, craving a transparent, regulatory framework while trying to accommodate the needs of their clients and shareholders to hold crypto assets. And while these institutions expand their participation in the still-nascent digital asset industry through custody, trading, and even new digital asset issuance, the desire for greater transparency and a global regulatory framework persists. This table, which contrasts the degree and effectiveness of regulators in digital asset space, highlights the differences in risk across most of the largest regulatory authorities, and brings to light one of the hidden challenges associated with investing in a spot Bitcoin ETF.
Relative Quality Scores – Global Regulatory Authorities
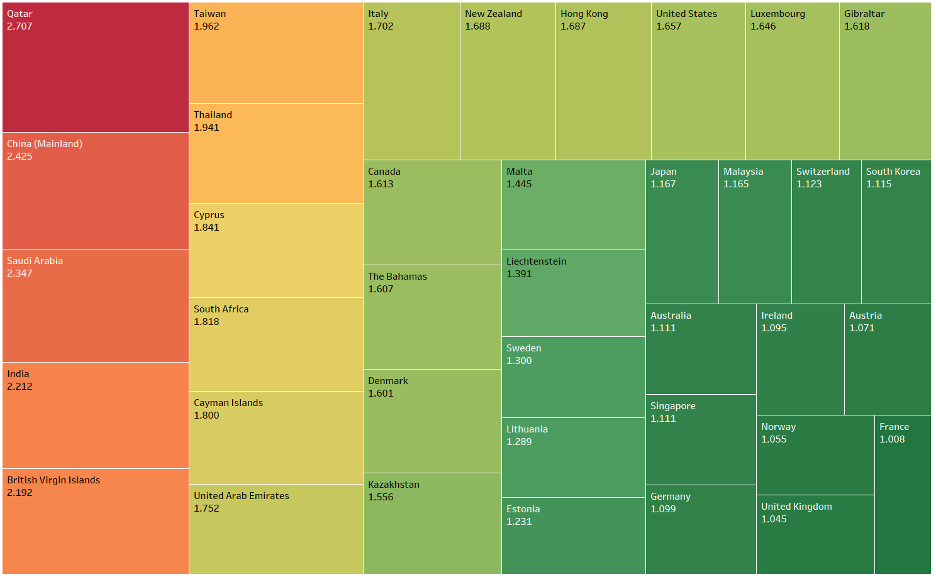 Source: CRB Monitor, Regulatory Authorities
Source: CRB Monitor, Regulatory Authorities
As crypto investors begin to wade into this vast sea of operational risk and volatility, there are a number of considerations that will be essential components of compliance and risk management beyond those required for typical ETF investing. Rather, it can be assumed that an investment in a spot Bitcoin ETF is akin, from a risk perspective, to an investment in Bitcoin itself. And it should not be overlooked that Bitcoin is actively traded on global exchanges of varying qualities and degrees of regulation, and as such lends itself to illicit activity.
Wondering what a Tier 1, Tier 2 or Tier 3 DARB is?
See our seminal ACAMS Today white paper Defining ‘Digital Asset-related Business’ and Digital-Asset Related Businesses - What Financial Institutions Need to Know